A TMAP sensor, or Temperature and Manifold Absolute Pressure sensor, is a combined sensor that integrates the functions of both a Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor and an Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor into a single unit. This sensor plays a crucial role in providing essential data to the engine control unit (ECU) for optimal engine performance and efficiency.

The MAP component of the TMAP sensor measures the pressure within the intake manifold of an engine, which helps the ECU determine the engine's load and adjust the air-fuel mixture accordingly for combustion. The IAT component of the sensor measures the temperature of the intake air entering the engine, allowing the ECU to adjust fuel injection and ignition timing based on the temperature of the air, which influences combustion efficiency.
By combining the functions of these two sensors into a single unit, the TMAP sensor simplifies the design and installation process, reduces the number of components in the engine system, and provides more accurate and real-time data to the ECU for precise engine control.
In summary, the TMAP sensor is a critical component in the engine management system of a vehicle, providing data on both intake manifold pressure and intake air temperature to optimize engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control.

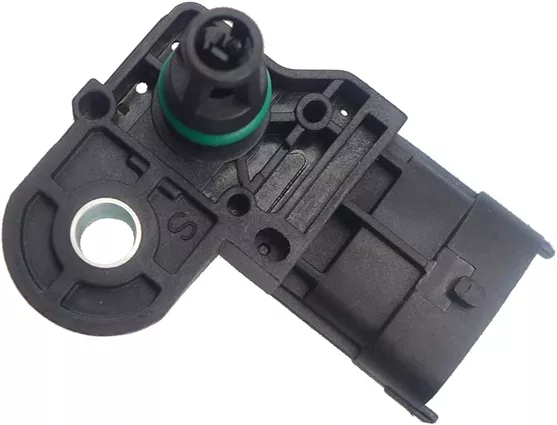
What Does A TMAP Sensor Do
A TMAP sensor, which stands for Temperature and Manifold Absolute Pressure sensor, combines the functions of both a Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor and an Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor into a single unit. Here is what a TMAP sensor does in a vehicle:
-
Measures Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP): The MAP component of the TMAP sensor measures the pressure inside the intake manifold of the engine. This information helps the engine control unit (ECU) determine the engine load and make adjustments to the fuel-air mixture and ignition timing for optimal engine performance.
-
Monitors Intake Air Temperature (IAT): The IAT component of the TMAP sensor measures the temperature of the incoming air into the engine. Understanding the temperature of the intake air is crucial for the ECU to calculate the appropriate fuel injection and ignition timing adjustments based on the density of the air entering the combustion chamber.
-
Optimizes Engine Performance: By providing accurate and real-time data on both the intake manifold pressure and intake air temperature, the TMAP sensor allows the ECU to fine-tune the fuel-air mixture and ignition timing to optimize engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control.
-
Enhances Engine Control: The TMAP sensor plays a vital role in ensuring that the engine operates efficiently under various driving conditions. It helps the ECU make precise adjustments to fuel delivery and ignition timing, leading to smoother operation and better overall performance of the vehicle.
-
Simplifies System Design: Combining the MAP and IAT functions into a single TMAP sensor simplifies the design and installation process in the engine system. It reduces the number of components required, streamlines the wiring, and provides more accurate and reliable data to the ECU for effective engine control.
Overall, the TMAP sensor is a critical component in modern engine management systems, offering integrated monitoring of both pressure and temperature to optimize engine operation and deliver improved performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control.
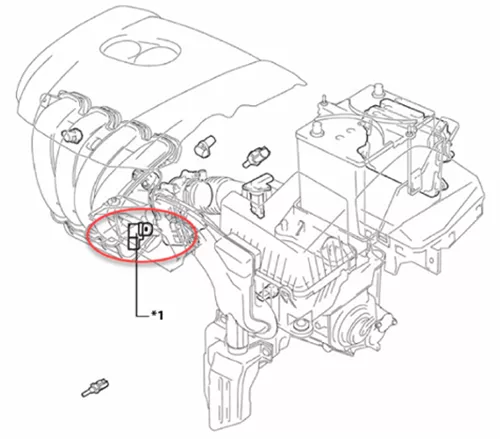
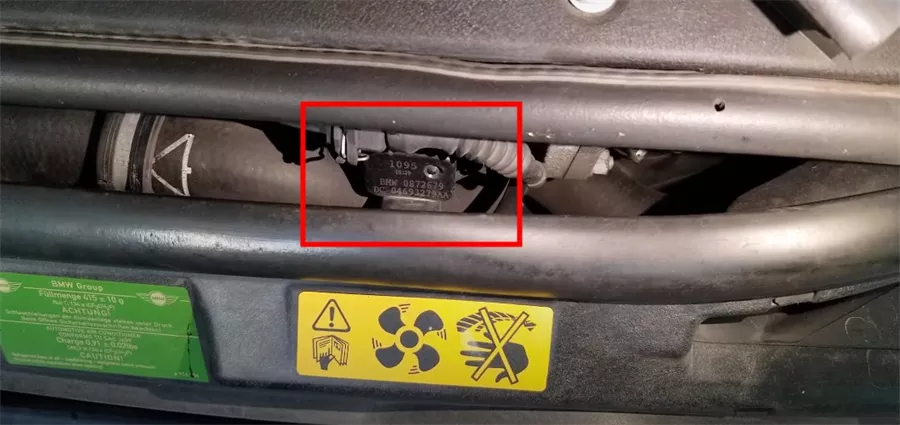
The Location of TMAP Sensor
The location of the TMAP (Temperature and Manifold Absolute Pressure) sensor can vary depending on the specific make and model of the vehicle. However, here are some general locations where you can typically find the TMAP sensor in most vehicles:
-
On the intake manifold: Like the standalone MAP sensor, the TMAP sensor is often located on or near the intake manifold. It may be mounted directly on the intake manifold or on a nearby vacuum hose or intake piping.
-
Near the throttle body: In some vehicles, the TMAP sensor can be found near the throttle body, which regulates the airflow into the engine. It may be positioned on the intake manifold or intake ducting leading to the throttle body.
-
Under the engine cover: In modern vehicles, the TMAP sensor may be located under the engine cover on top of the engine. You may need to remove the engine cover to access and locate the TMAP sensor.
-
Near the firewall: Depending on the vehicle's layout, the TMAP sensor could also be located near the firewall in the engine compartment, providing a stable mounting point for the sensor.
-
Consult the service manual: For precise information on the location of the TMAP sensor in your specific vehicle, it's best to refer to the vehicle's service manual or consult a professional mechanic. They can offer detailed guidance on the exact location and how to access the sensor for maintenance or replacement.
As the TMAP sensor combines the functions of the MAP and IAT sensors, it is crucial for providing accurate data to the engine control unit for optimized engine performance. Locating and ensuring the proper functioning of the TMAP sensor is essential to maintain the efficiency and performance of your vehicle.

The Difference between the MAP sensor and the TMAP sensor
The MAP sensor (Manifold Absolute Pressure sensor) and the TMAP sensor (Temperature and Manifold Absolute Pressure sensor) are both essential components in an engine's intake system, but they have some key differences:
-
Functionality:
- MAP Sensor: The MAP sensor measures the absolute pressure in the intake manifold of the engine. This data helps the engine control unit (ECU) to calculate the engine load and make necessary adjustments to the air-fuel mixture and ignition timing for optimal performance.
- TMAP Sensor: The TMAP sensor integrates the functions of a MAP sensor and an Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor into a single unit. Besides measuring the manifold pressure like the MAP sensor, the TMAP sensor also monitors the temperature of the incoming air so that the ECU can adjust fuel injection and ignition timing based on air density for efficient engine operation.
-
Components:
- MAP Sensor: A standalone MAP sensor only measures manifold pressure.
- TMAP Sensor: Combines the functions of a MAP sensor and an IAT sensor in one unit, measuring both pressure and temperature in the intake system.
-
Integration:
- MAP Sensor: The MAP sensor is a separate component that measures only the manifold pressure.
- TMAP Sensor: The TMAP sensor combines the functions of the MAP sensor and the IAT sensor into one sensor unit, streamlining the design and installation process by reducing the number of components in the system.
-
Installation:
- MAP Sensor: Typically installed on or near the intake manifold.
- TMAP Sensor: Also usually located on or near the intake manifold but integrates temperature sensing capabilities along with pressure measurement.
-
Benefits:
- MAP Sensor: Provides crucial data on manifold pressure for engine load calculations.
- TMAP Sensor: Offers the benefits of both pressure measurement and intake air temperature monitoring, allowing for more precise adjustments to fuel injection and ignition timing for optimal engine performance and efficiency.
In summary, while the MAP sensor focuses solely on measuring manifold pressure, the TMAP sensor expands its functionality by combining pressure measurement with intake air temperature sensing, providing more comprehensive data to the engine control unit for improved engine control and performance optimization.

What Is A Map Sensor And How Does It Work
A Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor is an essential component in a vehicle's engine management system. It measures the pressure inside the intake manifold of an engine and provides critical data to the engine control unit (ECU). Here is how a MAP sensor works:
-
Function: The MAP sensor's primary function is to measure the absolute pressure inside the intake manifold. This information helps the ECU determine the engine load in real-time.
-
Location: The MAP sensor is typically located on or near the intake manifold of the engine to ensure it accurately measures the pressure of the air entering the engine.
-
Pressure Measurement: The sensor utilizes a vacuum port that is connected to the intake manifold. As the engine operates, the pressure in the intake manifold fluctuates based on factors like throttle position, engine speed, and load.
-
Analog or Digital Output: The MAP sensor can provide either analog or digital output signals to the ECU. The sensor converts the pressure measurements into an electrical signal that the ECU can interpret.
-
Engine Load Calculation: By monitoring the pressure in the intake manifold, the MAP sensor helps the ECU calculate the engine load. The ECU uses this data to determine the optimal air-fuel ratio and ignition timing for efficient combustion.
-
Performance Optimization: With accurate and real-time data from the MAP sensor, the ECU can make adjustments to fuel delivery and ignition timing, optimizing engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control.
-
Diagnostic Tool: In case of any issues with the engine, the MAP sensor's data can be used for diagnostic purposes to identify problems such as engine misfires, rough idling, or poor acceleration.
In essence, the MAP sensor plays a crucial role in the engine management system by providing essential pressure data to the ECU. This data enables the ECU to adjust various parameters to ensure the engine operates efficiently under different driving conditions.


