Circuit boards, those intricate and fascinating components of electronic devices, are most often found sporting a vibrant green color.
But have you ever stopped to wonder, why are circuit boards green? In this article, we will look at the reasons for green circuit board together.
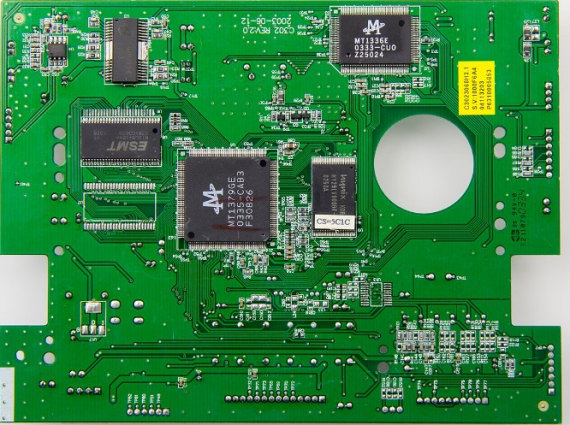
Circuit boards are typically green due to the solder mask that is applied to them for several practical and historical reasons:
-
Contrast: The green color of the solder mask provides a good contrast for easier visibility of white silkscreen markings (indicating component placement and orientation) and copper traces on the board. This color contrast aids in the visual inspection and debugging of the circuit board during assembly and maintenance processes.
-
Manufacturing Standard: Green solder mask has become a standard in the electronics industry due to its widespread use and familiarity. This standardization simplifies the manufacturing process and helps ensure consistency and compatibility across different manufacturers and components.
-
Aesthetic Appeal: Over time, the association of green circuit boards with electronics has become ingrained in popular culture and consumer expectations. The green color has become symbolic of technology and innovation in the collective consciousness.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Green solder mask is readily available and cost-effective, making it a practical choice for manufacturers looking to produce circuit boards efficiently and affordably. The availability and affordability of green solder mask contribute to its widespread use in the industry.
-
Thermal Properties: Green solder mask offers good thermal performance, helping to dissipate heat generated during operation and maintaining the stability of electronic components on the board. This heat dissipation property is beneficial for maintaining the reliability and performance of the circuit board.
-
UV Protection: The green solder mask on circuit boards provides a level of UV protection, shielding the underlying components and traces from potential damage caused by exposure to ultraviolet light.
While green is the most common color for solder mask on circuit boards, other colors such as red, blue, black, and white are also used for specific applications or design preferences. Ultimately, the choice of solder mask color is influenced by factors such as visibility, industry standards, cost, thermal properties, and aesthetic considerations.
What Are Green Circuit Boards Made of
Green circuit boards, also known as printed circuit boards (PCBs), consist of various layers of materials that serve different functions in the construction of the board. Here are the common materials used in the construction of green circuit boards:
-
Substrate Material:
- FR-4 (Flame Retardant-4): FR-4 is a widely used substrate material for PCBs. It is a type of woven fiberglass cloth impregnated with an epoxy resin binder. FR-4 is known for its durability, electrical insulation properties, and resistance to heat. It provides mechanical support and electrical insulation to the board.
-
Copper Layers:
- Thin copper layers are bonded to both sides of the substrate material. These copper layers serve as the conductive pathways for electrical signals on the circuit board. The copper is typically etched to create the circuit traces and pads for components.
-
Solder Mask:
- The green color on circuit boards comes from the solder mask, which is a protective layer applied over the copper traces to prevent short circuits and oxidation. The solder mask is typically made of epoxy-based liquid photoimageable solder mask materials that are applied and then cured to a solid form, creating the green surface.
-
Silkscreen:
- The white markings and labels on the circuit board are added using a silkscreen layer. The silkscreen makes it easier to identify components, orientation, and other information on the board.
-
Plating and Surface Finish:
- The exposed copper traces and pads are often coated with a surface finish to protect them from oxidation and ensure good solderability. Common surface finishes include HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), OSP (Organic Solderability Preservatives), and others.
-
Vias and Pads:
- Vias are plated holes that allow electrical connections between different layers of the PCB. Pads provide the connection points for components to be soldered onto the board.
These materials are carefully engineered and layered together to create functional and reliable circuit boards for electronic devices. The green color of PCBs primarily comes from the solder mask layer, which is a critical component providing both protection and insulation on the board.
Does the Color of a Circuit Board Matter
The color of a circuit board, whether it's green, red, blue, black, or any other color, does not impact the functionality or performance of the board. The color is primarily a matter of aesthetics and design preference rather than a technical consideration. However, there are a few aspects to consider regarding the color of the circuit board:
-
Aesthetics: The color of a circuit board can affect its visual appeal and how it fits the overall design of a product. Some companies or individuals may choose a specific color to align with their brand or to create a certain visual aesthetic.
-
Visibility and Contrast: Certain colors, such as green, provide good contrast for component markings (silkscreen) and copper traces on the board. This can aid in assembly, repair, and maintenance processes by making it easier to identify components or trace paths.
-
UV Protection: Some colors may offer better UV protection than others. For instance, black circuit boards may provide better protection against UV radiation compared to lighter colors. This can be important in applications where UV exposure is a concern.
-
Heat Absorption: Dark-colored circuit boards may absorb more heat compared to light-colored ones. While this might not be a significant factor in many applications, it could have implications for certain high-temperature environments.
-
Customization: Some manufacturers or designers may use different colors as a way to differentiate their products or signal specific product lines.
In summary, while the color of a circuit board does not impact its functionality, it can have implications for aesthetics, visibility, UV protection, heat absorption, and customization. Ultimately, the choice of board color is often based on personal or branding preferences, as well as practical considerations related to the specific application and design requirements.
Reasons for Different Colors of Circuit Boards
Circuit boards come in various colors, such as green, red, blue, black, yellow, and white. The choice of color for circuit boards can be influenced by several factors, including:
-
Aesthetics and Branding: Some companies prefer to use specific colors for their circuit boards to align with their brand identity or to create a certain aesthetic appeal. The color choice can reflect the company's branding and design preferences.
-
Functionality and Visibility: Certain colors provide better visibility and contrast for components, markings, and traces on the circuit board. For example, white silkscreen markings might stand out more on a dark-colored circuit board, making it easier to read and identify components.
-
UV Protection: Dark-colored circuit boards, such as black, may offer better protection against ultraviolet (UV) radiation compared to lighter-colored boards. This can be important for applications where UV exposure can degrade the materials or affect performance.
-
Heat Dissipation: The color of a circuit board can affect its ability to dissipate heat. Dark-colored circuit boards tend to absorb more heat compared to lighter-colored boards. In high-temperature environments, the choice of color can impact thermal management.
-
Industry Standards: Certain industries or applications may have standard color codes for circuit boards. These standards help ensure consistency and compliance with industry practices.
-
Customization and Differentiation: Using different colors for circuit boards can help differentiate products or signal specific product lines within a company's portfolio. This customization can be a way to visually distinguish products in competitive markets.
-
Supplier Availability: The availability of certain color options from PCB manufacturers may influence the choice of color for circuit boards. Some colors may be more readily available or cost-effective than others.
-
Consumer Preferences: In some cases, consumer preferences or market trends may influence the choice of circuit board colors. Manufacturers may cater to consumer expectations or preferences when deciding on the color of circuit boards for consumer electronics products.
Overall, the color of a circuit board is a design choice that can impact aesthetics, functionality, visibility, heat dissipation, UV protection, and customization. Designers and manufacturers consider these factors, along with industry standards, branding considerations, and practical requirements, when selecting the color for a circuit board in a particular application.


